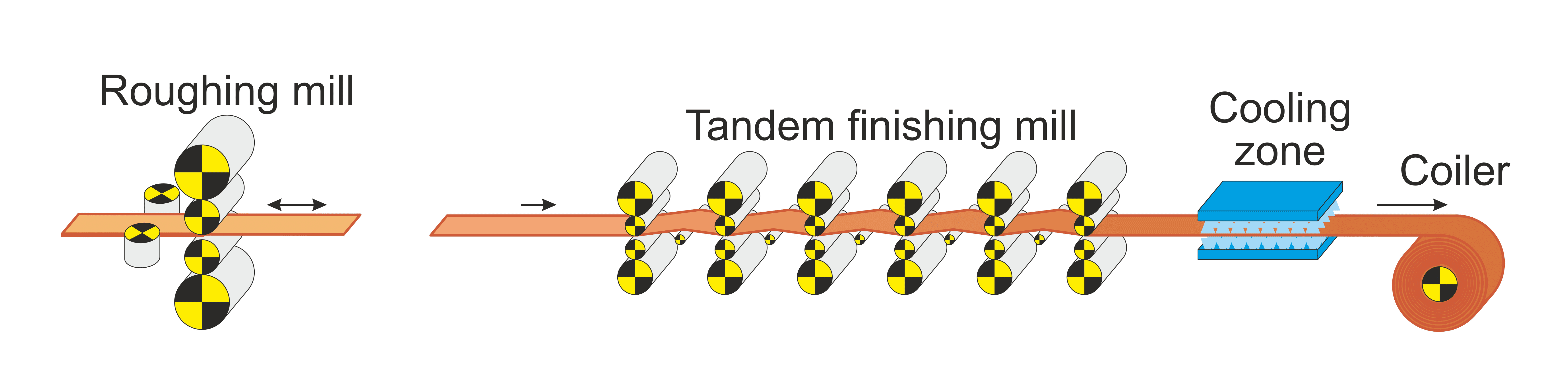
Hot Strip Mills
Forging Strength. Delivering Precision.
Hot Strip Mills
Forging Strength. Delivering Precision.

The Strip Mill represents the most productive solution for flat rolled products. It provides the highest level of productivity together with a large product mix and outstanding quality. We are proud to present ourselves as an eminent enterprise for turnkey installation of Strip Mills.

The Strip Mill represents the most productive solution for flat rolled products. It provides the highest level of productivity together with a large product mix and outstanding quality. We are proud to present ourselves as an eminent enterprise for turnkey installation of Strip Mills.
Hot Strip Mill Capabilities
For achieving these demanding requirements, many important features are incorporated in the modern conventional Hot Strip Mills. Some of these are described below .
Modern hot strip mills are equipped with energy efficient walking beam furnaces which are normally computerized controlled. These reheating furnaces uniformly heat the slabs to the target temperatures at the required production rates and without skid marks and without cold spots. These furnaces are capable of receiving cold or hot slabs as the charge material in the furnace.
De-scaler is must in hot strip mills for attaining good surface quality. Present day descales employ state of the art nozzle technology with highly effective application of high pressure water (up to 400 bars). Descales are usually of closed design to prevent water from escaping.
A slab sizing press in the roughing mill area has the technological advantage over a conventional edger. Besides large width reductions (up to 350 mm), it results into a distinctly better through forming of the slab right to its centre.
Coil box enables a shorter distance between the roughing mill and finishing mill. It also minimizes the temperature drop of the transfer bar entering the finishing mill.

Hot Strip Mill Capabilities
For achieving these demanding requirements, many important features are incorporated in the modern conventional Hot Strip Mills. Some of these are described below .
Modern hot strip mills are equipped with energy efficient walking beam furnaces which are normally computerized controlled. These reheating furnaces uniformly heat the slabs to the target temperatures at the required production rates and without skid marks and without cold spots. These furnaces are capable of receiving cold or hot slabs as the charge material in the furnace.
De-scaler is must in hot strip mills for attaining good surface quality. Present day descales employ state of the art nozzle technology with highly effective application of high pressure water (up to 400 bars). Descales are usually of closed design to prevent water from escaping.
A slab sizing press in the roughing mill area has the technological advantage over a conventional edger. Besides large width reductions (up to 350 mm), it results into a distinctly better through forming of the slab right to its centre.
Coil box enables a shorter distance between the roughing mill and finishing mill. It also minimizes the temperature drop of the transfer bar entering the finishing mill.

The control of the gap between the work rolls, and in other words the strip thickness, is made in two steps with two control modules . The first module is called AGC while the second module is known as HGC. AGC receives thickness set points from a higher level system. It calculates and compensates for such things as roll wear, heat expansion in the rolls, stretch of the strand and other immeasurable quantities which affects the gap.
Excellent width accuracy can be achieved by providing the hydraulic AWC system on the vertical edger from head end to the tail end of the strip. Hydraulic cylinder operated width control system is used. This system work as the short stroke control for the head end and tail end of the strip and as a AWC system for rest of the strip. Electro mechanical servo valves precisely control the hydraulic cylinder position.
In a hot strip mill, the backup rolls have a large diameter for supporting the work roll and prevent it from bending. But in practice even backup rolls get bent when the force on the bearing housing becomes larger. This makes the force applied on the work roll higher closer to the bearing housing and smaller at the middle of the roll.
In a hot strip mill, the backup rolls have a large diameter for supporting the work roll and prevent it from bending. But in practice even backup rolls get bent when the force on the bearing housing becomes larger. This makes the force applied on the work roll higher closer to the bearing housing and smaller at the middle of the roll.

The control of the gap between the work rolls, and in other words the strip thickness, is made in two steps with two control modules . The first module is called AGC while the second module is known as HGC. AGC receives thickness set points from a higher level system. It calculates and compensates for such things as roll wear, heat expansion in the rolls, stretch of the strand and other immeasurable quantities which affects the gap.
Excellent width accuracy can be achieved by providing the hydraulic AWC system on the vertical edger from head end to the tail end of the strip. Hydraulic cylinder operated width control system is used. This system work as the short stroke control for the head end and tail end of the strip and as a AWC system for rest of the strip. Electro mechanical servo valves precisely control the hydraulic cylinder position.
In a hot strip mill, the backup rolls have a large diameter for supporting the work roll and prevent it from bending. But in practice even backup rolls get bent when the force on the bearing housing becomes larger. This makes the force applied on the work roll higher closer to the bearing housing and smaller at the middle of the roll.
In a hot strip mill, the backup rolls have a large diameter for supporting the work roll and prevent it from bending. But in practice even backup rolls get bent when the force on the bearing housing becomes larger. This makes the force applied on the work roll higher closer to the bearing housing and smaller at the middle of the roll.